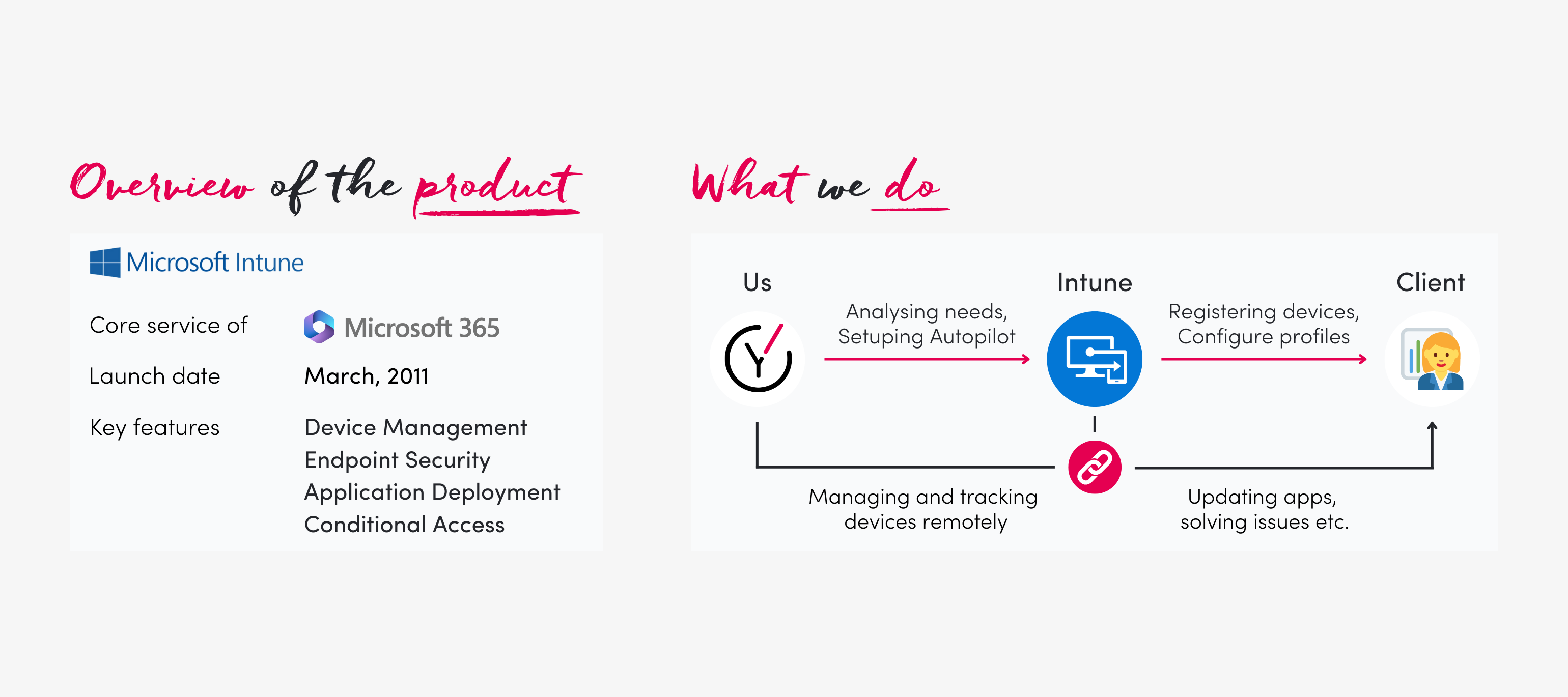
Let's delve into modern IT management and explore how Microsoft Intune is reshaping the landscape for organizations, ensuring streamlined operations and robust security measures. Microsoft Intune, introduced in March 2011, has since evolved into a powerhouse of IT management capabilities, ingrained in the core services of Microsoft 365. It offers a comprehensive suite of features, including device management, endpoint security, application deployment, and conditional access control. The beauty lies in its seamless integration within the Microsoft 365 ecosystem, enabling organizations to manage various devices and efficiently comply with organizational policies.
Key Features of Microsoft Intune
Device Management
Microsoft Intune allows centralized device management, enabling IT administrators to provision, configure, and manage devices across various platforms, including Windows, iOS, Android, and macOS. This centralized approach simplifies device onboarding, policy enforcement, and troubleshooting.
Endpoint Security
With Intune, organizations can bolster their endpoint security by applying security policies, enforcing encryption, implementing threat protection, and regularly monitoring and managing security updates. This helps mitigate potential security risks and safeguard sensitive data.
Application Deployment
Intune facilitates seamless application deployment, allowing IT administrators to distribute and manage applications across devices efficiently. Whether pushing critical business apps or security updates, Intune ensures that suitable applications are available on the proper devices.
Conditional Access
Conditional Access is a powerful feature of Intune that enables organizations to define and enforce access policies based on specific conditions, such as location, device compliance, or user roles. This provides an additional layer of security by ensuring that Access to sensitive data and resources is granted only to authorized and compliant users.